Foundation框架允许你利用文件系统对文件或目录执行基本操作。这些基本操作是由NSFileManager类提供的,这个类的方法具有如下功能:
- 创建一个新文件
- 从现有文件中读取数据
- 将数据写入文件
- 重命名文件
- 删除文件
- 测试文件是否存在
- 确定文件的大小和其他属性
- 复制文件
- 测试两个文件的内容是否相同
上面的多数方法也可以对目录进行操作。例如,创建目录、读取目录的内容,或者删除目录。另一个重要特性是链接文件,即同一个文件存在两个不同的名字,有时甚至位于不同的目录中。
使用NSFileHandle类提供的方法,可以打开文件并对文件执行多次读/写操作。NSFileHandle类的方法可以实现如下功能:
- 打开一个文件,执行读、写或更新(读取和写入)操作。
- 在文件中查找指定位置。
- 从文件中读取特定数目的字节,或将指定数目的字节写入文件中。
NSFileHandle类提供的方法也可用于各种设备或套接字。
NSURL类允许在应用中使用URL方法。
NSBundle类提供了允许在应用中使用包(bundle)的方法,包括搜索包中的特定资源(如JPEG图片)。
| 常用的NSFileManager方法 | |
| 方法 | 描述 |
| -(NSData *) contentsAtPath: path | 从一个文件中读取数据 |
| -(BOOL) createFileAtPath: path contents: (NSData *) data attributes: attr | 向一个文件写入数据 |
| -(BOOL) removeItemAtPath: path error: err | 删除一个文件 |
| -(BOOL) moveItemAtPath: from toPath: to error: err | 重命名或者移动一个文件(to不能是已存在的) |
| -(BOOL) copyItemAtPath: from toPath: to error: err | 复制文件(to不能是已存在的) |
| -(BOOL) contentsEqualAtPath: path1 andPath: path2 | 比较两个文件的内容 |
| -(BOOL) fileExistsAtPath: path | 测试文件是否存在 |
| -(BOOL) isReadableFileAtPath: path | 测试文件是否存在,并且是否能执行读操作 |
| -(BOOL) isWritableFileAtPath: path | 测试文件是否存在,并且是否能执行写操作 |
| -(NSDictionary *) attributesOfItemAtPath: path error: err | 获取文件的属性,所有属性对应的词典中的键都定义在<Foundation/NSFileManager.h>中,例如,表示文件大小的键为NSFileSize |
| -(BOOL) setAttributesOfItemAtPath: attr error: err | 更改文件的属性 |
| -(NSString *) currentDirectoryPath | 获取当前目录 |
| -(BOOL) changeCurrentDirectoryPath: path | 更改当前目录 |
| -(BOOL) copyItemAtPath: from toPath: to error: err |
复制目录结构(to不能是已存在的) |
| -(BOOL) createDirectoryAtPath: path withIntermediate Directories: (BOOL) flag attributes: attr |
创建一个新目录 |
| -(BOOL) fileExistsAtPath: path is Directory: (BOOL *) flag |
测试文件是不是目录(flag中存储结果YES/NO) |
| -(NSArray *) contentsOfDirectoryAtPath: path error: err |
列出目录内容 |
| -(NSDirectoryEnumerator *) enumeratorAtPath: path |
枚举目录内容 |
| -(BOOL) removeItemAtPath: path error: err |
删除空目录 |
| -(BOOL) moveItemAtPath: from toPath: to error: err | 重命名或移动一个目录(to不能是已存在的) |
说明:
path、path1、path2、from和to都是NSString对象,attr是一个NSDictionary对象;err是一个指向NSError对象的指针,能提供更多的错误信息。如果err指定为NULL,就会采取默认的行为,具有BOOL返回值的方法,即如果操作成功,就会返回YES;否则就会返回NO。
主目录的完整路径为/users/用户名
特殊的代字符(~)作为用户主目录的缩写。~xxx等价于/users/xxx
Foundation的文件处理不支持其他特殊的UNIX风格,如表示当前目录的“.”和表示父目录的“..”
小知识:
示例一
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSString *fName = @"testfile";
NSFileManager *fm;
NSDictionary *attr;
// 需要创建文件管理器的实例
fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
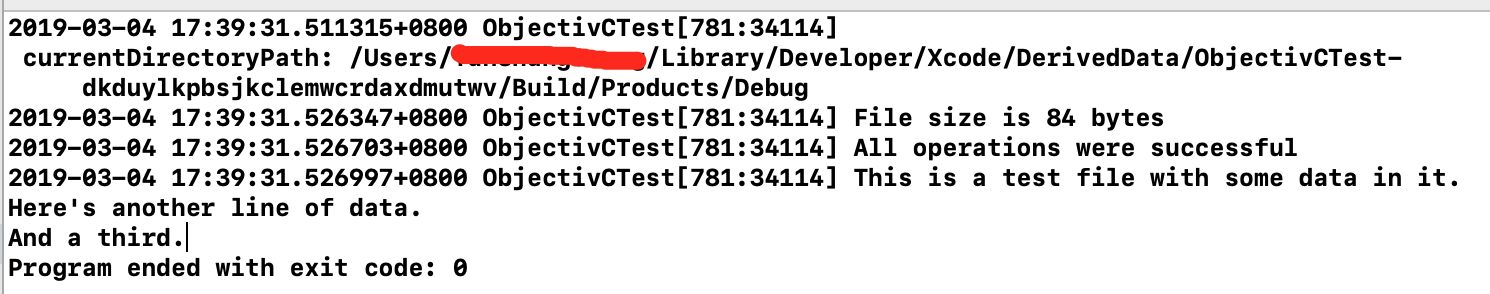
NSLog(@"\n currentDirectoryPath: %@", [fm currentDirectoryPath]);
// 首先确认测试文件存在
if ([fm fileExistsAtPath: fName] == NO) {
NSLog(@"File does't exist");
return 1;
}
// 创建一个副本
if ([fm copyItemAtPath: fName toPath: @"newfile" error: NULL] == NO) {
NSLog(@"File Copy failed!");
return 2;
}
// 测试两个文件是否一致
if ([fm contentsEqualAtPath: fName andPath: @"newfile"] == NO) {
NSLog(@"Files are Not Equal!");
return 3;
}
// 重命名副本
if ([fm moveItemAtPath: @"newfile" toPath: @"newfile2" error: NULL] == NO) {
NSLog(@"File rename Failed");
return 4;
}
// 获取newfile2的大小
if ((attr = [fm attributesOfItemAtPath: @"newfile2" error: NULL]) == nil) {
NSLog(@"Couldn't get file attributes!");
return 5;
}
NSLog(@"File size is %llu bytes",
[[attr objectForKey: NSFileSize] unsignedLongLongValue]);
// 最后删除原始文件
if ([fm removeItemAtPath: fName error: NULL] == NO) {
NSLog(@"file remove failed");
return 6;
}
NSLog(@"All operations were successful");
// 显示新创建的文件内容
NSLog(@"%@", [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:
@"newfile2" encoding: NSUTF8StringEncoding error: NULL]);
}
return 0;
}
示例二:目录操作
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSString *dirName = @"testdir";
NSString *path;
NSFileManager *fm;
// 需要创建文件管理器的实例
fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
// 获取当前目录
path = [fm currentDirectoryPath];
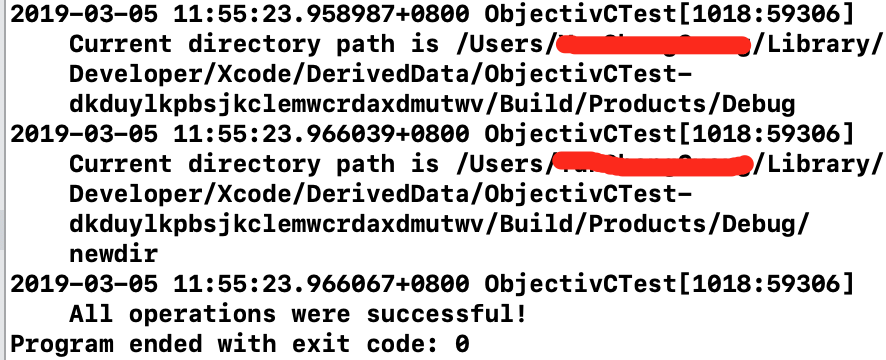
NSLog(@"Current directory path is %@", path);
// 创建一个新目录
if ([fm createDirectoryAtPath: dirName withIntermediateDirectories: YES
attributes:nil error: NULL] == NO) {
NSLog(@"Coundn't create directory!");
return 1;
}
// 重命名新的目录
if ([fm moveItemAtPath: dirName toPath: @"newdir" error: NULL] == NO) {
NSLog(@"Directory rename failed!");
return 2;
}
// 更改目录到新的目录
if ([fm changeCurrentDirectoryPath: @"newdir"] == NO) {
NSLog(@"Change directory failed!");
return 3;
}
// 获取并显示当前的工作目录
path = [fm currentDirectoryPath];
NSLog(@"Current directory path is %@", path);
NSLog(@"All operations were successful!");
}
return 0;
}
在iOS设备上,程序是运行在沙盒中,如果在设备中运行这个程序,会看到当前目录是/,这说明应用的根目录是在运行它的沙盒中,并不是整个iOS设备文件目录的根。
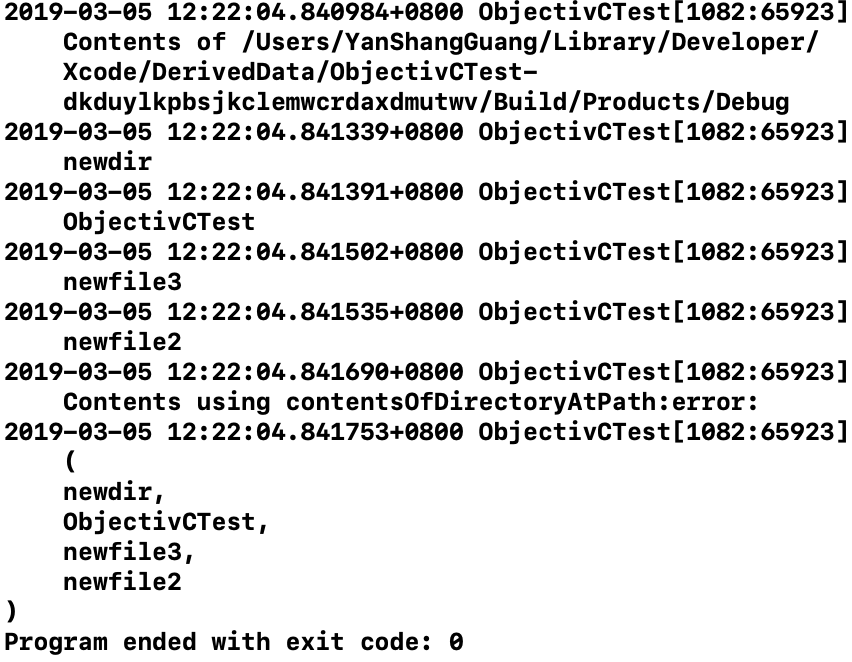
示例三:枚举目录
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSString *path;
NSFileManager *fm;
NSDirectoryEnumerator *dirEnum;
NSArray *dirArray;
fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
// 获取当前工作目录
path = [fm currentDirectoryPath];
// 枚举目录
// enumeratorAtPath 这个方法会递归遍历目录
dirEnum = [fm enumeratorAtPath: path];
NSLog(@"Contents of %@", path);
BOOL flag;
while ((path = [dirEnum nextObject]) != nil) {
NSLog(@"%@", path);
// 如果是子目录,则跳过遍历
[fm fileExistsAtPath: path isDirectory: &flag];
if (flag == YES)
[dirEnum skipDescendants];
}
// 另一种枚举目录的方法,非递归遍历
dirArray = [fm contentsOfDirectoryAtPath:
[fm currentDirectoryPath] error: NULL];
NSLog(@"Contents using contentsOfDirectoryAtPath:error:");
//for (path in dirArray)
//NSLog(@"%@", path);
// 打印数组
NSLog(@"%@", dirArray);
}
return 0;
}