@class指令
post by:追风剑情 2019-2-22 11:39
示例一:使用@class指令
XYPoint.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface XYPoint : NSObject @property int x, y; -(void) setX: (int) xVal andY: (int) yVal; @end
XYPoint.m
#import "XYPoint.h"
@implementation XYPoint
@synthesize x, y;
-(void) setX: (int) xVal andY: (int) yVal
{
x = xVal;
y = yVal;
}
@end
Rectangle.h
// // Rectangle.h // ObjectivCTest // // Created by XXX on 2019/2/21. // Copyright © 2019 XXX. All rights reserved. // #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> // 这里用@class指令告诉编译器XYPoint是个类,比导入头文件效率高。 @class XYPoint; @interface Rectangle : NSObject @property int width, height; -(XYPoint *) origin; -(void) setOrigin: (XYPoint *) pt; -(int) area; -(int) perimeter; -(void) setWidth: (int) w andHeight: (int) h; @end
Rectangle.m
#import "Rectangle.h"
@implementation Rectangle
@synthesize width, height;
// 矩形的原点坐标
XYPoint *origin;
-(XYPoint *) origin
{
return origin;
}
-(void) setOrigin: (XYPoint *) pt
{
origin = pt;
}
-(void) setWidth: (int) w andHeight: (int) h
{
width = w;
height = h;
}
// 求在积
-(int) area
{
return width * height;
}
// 求周长
-(int) perimeter
{
return (width + height) * 2;
}
@end
main.m
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Rectangle.h"
#import "XYPoint.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
Rectangle *myRect = [[Rectangle alloc] init];
XYPoint *myPoint = [[XYPoint alloc] init];
[myPoint setX: 100 andY: 200];
[myRect setWidth: 5 andHeight: 8];
myRect.origin = myPoint;
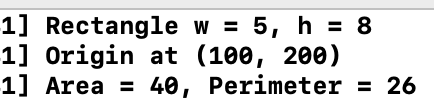
NSLog(@"Rectangle w = %i, h = %i", myRect.width, myRect.height);
// myRect.origin.x等价于[[myRect origin] x]
NSLog(@"Origin at (%i, %i)", myRect.origin.x, myRect.origin.y);
NSLog(@"Area = %i, Perimeter = %i",
[myRect area], [myRect perimeter]);
}
return 0;
}
示例二:不能使用@class的情况
XYPoint.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface XYPoint : NSObject @property int x, y; -(void) setX: (int) xVal andY: (int) yVal; @end
XYPoint.m
#import "XYPoint.h"
@implementation XYPoint
@synthesize x, y;
-(void) setX: (int) xVal andY: (int) yVal
{
x = xVal;
y = yVal;
}
@end
Rectangle.h
// // Rectangle.h // ObjectivCTest // // Created by XXX on 2019/2/21. // Copyright © 2019 XXX. All rights reserved. // #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> // 这里用@class指令告诉编译器XYPoint是个类,比导入头文件效率高。 //@class XYPoint; // 因为Rectangle.m中调用了XYPoint类的方法,编译器需要知道XYPoint的更多信息, // 所以必须导入头文件,而不能使用@class指令 #import "XYPoint.h" @interface Rectangle : NSObject @property int width, height; -(XYPoint *) origin; -(void) setOrigin: (XYPoint *) pt; -(int) area; -(int) perimeter; -(void) setWidth: (int) w andHeight: (int) h; @end
Rectangle.m
#import "Rectangle.h"
@implementation Rectangle
@synthesize width, height;
// 矩形的原点坐标
XYPoint *origin;
-(XYPoint *) origin
{
return origin;
}
-(void) setOrigin: (XYPoint *) pt
{
// 这里创建了XYPoint实例,
// 那么在Rectangle.h就必须导入XYPoint.h,而不能用@class指令单纯的告诉编译器这是个类,
// 因为编译器除了要知道XYPoint是个类之外,还是要了解XYPoint的其他信息(比如方法名及函数),所以必须导入头文件。
if (! origin)
origin = [[XYPoint alloc] init];
origin.x = pt.x;
origin.y = pt.y;
}
-(void) setWidth: (int) w andHeight: (int) h
{
width = w;
height = h;
}
// 求在积
-(int) area
{
return width * height;
}
// 求周长
-(int) perimeter
{
return (width + height) * 2;
}
@end
main.m
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Rectangle.h"
#import "XYPoint.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
Rectangle *myRect = [[Rectangle alloc] init];
XYPoint *myPoint = [[XYPoint alloc] init];
[myPoint setX: 100 andY: 200];
[myRect setWidth: 5 andHeight: 8];
myRect.origin = myPoint;
NSLog(@"Rectangle w = %i, h = %i", myRect.width, myRect.height);
// myRect.origin.x等价于[[myRect origin] x]
NSLog(@"Origin at (%i, %i)", myRect.origin.x, myRect.origin.y);
NSLog(@"Area = %i, Perimeter = %i",
[myRect area], [myRect perimeter]);
}
return 0;
}
评论:
发表评论: