RLE压缩算法
post by:追风剑情 2016-4-16 15:11
RLE(Run Length Encoding)压缩算法即行程长度压缩算法,也称游程长度压缩算法,是最早出现、也是最简单的无损数据压缩算法。RLE压缩算法对黑白图像和基于调色板的单调图像有很高的压缩效率,不仅常用于处理图像数据,在传真机上也得到了广泛的应用。
压缩格式
[长度标识位] [数据块]
长度标识位通常用一个字节标识,字节最高位为1表示后面的数据块是连续重复数据。字节最高位为0表示后面的数据块是非连续数据。把最高位除开,只有剩下的7位用来表示数据长度(即最大值是127)。
重复数据: 连续出现次数2次以上。(例如: 65, 65, 65, ...)
以下是RLE算法实现代码
using System;
/// <summary>
/// 行程长度压缩算法 RLE(Run Length Encoding)
/// 最简单的无损数据压缩算法
/// </summary>
public class RLE
{
/// <summary>
/// 压缩
/// </summary>
/// <param name="inbuf">原始数据</param>
/// <returns>压缩后的数据</returns>
public static byte[] Encode(byte[] inbuf)
{
int encSize = 0;
int inbufPos = 0;
int inBuffSize = inbuf.Length;
byte[] buff = new byte[inBuffSize];
while (inbufPos < inBuffSize)
{
byte count = 0;
if (IsRepetitionStart(inbuf, inbufPos))
{
count = GetRepetitionCount(inbuf, inbufPos);
//长度字节最高位设置为1
buff[encSize++] = (byte)(count | 0x80);
buff[encSize++] = inbuf[inbufPos];
inbufPos += count;
}
else
{
count = GetNonRepetitionCount(inbuf, inbufPos);
buff[encSize++] = count;
//逐个复制这些数据
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
buff[encSize++] = inbuf[inbufPos++];
}
}
}
byte[] outbuf = new byte[encSize];
Array.Copy(buff, 0, outbuf, 0, encSize);
return outbuf;
}
/// <summary>
/// 解压
/// </summary>
/// <param name="inbuf">压缩数据</param>
/// <param name="outBuffSize">输出缓冲区大小</param>
/// <returns>解压后的数据</returns>
public static byte[] Decode(byte[] inbuf, int outBuffSize = -1)
{
int i;
int decSize = 0;
int count = 0;
int inbufPos = 0;
int inbufSize = inbuf.Length;
if (-1 == outBuffSize)
outBuffSize = inbufSize * 5;
byte[] buff = new byte[outBuffSize];
while (inbufPos < inbufSize)
{
byte sign = inbuf[inbufPos++];
count = sign & 0x3F;
//输出缓冲区空间不够了
if (decSize + count > outBuffSize)
{
Console.WriteLine("错误: 输出缓冲区空间不够");
return null;
}
if ((sign & 0x80) == 0x80)//连续重复数据标志
{
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
buff[decSize++] = inbuf[inbufPos];
}
inbufPos++;
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
buff[decSize++] = inbuf[inbufPos++];
}
}
}
byte[] outbuf = new byte[decSize];
Array.Copy(buff, 0, outbuf, 0, decSize);
return outbuf;
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否连续三个字节数据相同
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
static bool IsRepetitionStart(byte[] src, int srcLeft)
{
if (srcLeft + 3 >= src.Length)
return false;
int byte1 = src[srcLeft];
int byte2 = src[srcLeft + 1];
int byte3 = src[srcLeft + 2];
return (byte1 == byte2 && byte1 == byte3);
}
static byte GetRepetitionCount(byte[] src, int srcPos)
{
int endLeft = srcPos + 127;
if (endLeft >= src.Length)
endLeft = src.Length - 1;
byte count = 1;
for (int i = srcPos; i < endLeft; i++)
{
if (src[i] != src[i + 1])
break;
count++;
}
return count;
}
static byte GetNonRepetitionCount(byte[] src, int srcPos)
{
//只剩最后两字节数据了
if (src.Length - srcPos <= 3)
return 2;
int endLeft = srcPos + 127;
if (endLeft >= src.Length)
endLeft = src.Length - 1;
byte count = 0;
for (int i = srcPos; i <= endLeft; i++)
{
if (IsRepetitionStart(src, i))
break;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
测试
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
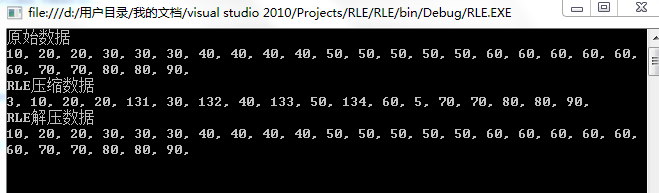
//测试数据
byte[] data = new byte[] {
10,
20, 20,
30, 30, 30,
40, 40, 40, 40,
50, 50, 50, 50, 50,
60, 60, 60, 60, 60, 60,
70, 70, 80, 80, 90
};
Console.WriteLine("原始数据");
for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++)
Console.Write(data[i]+", ");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("RLE压缩数据");
byte[] en_data = RLE.Encode(data);
for (int i = 0; i < en_data.Length; i++)
Console.Write(en_data[i] + ", ");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("RLE解压数据");
byte[] de_data = RLE.Decode(en_data);
for (int i = 0; i < de_data.Length; i++)
Console.Write(de_data[i] + ", ");
Console.Read();
}
}
运行效果
评论:
发表评论: