Shader——创建Phong高光类型
post by:追风剑情 2015-9-19 19:28
Phong高光模型是最基础且表现最友好的调光类型。它会计算出光在物体表面的反射方向与观察者视线方向之间的对比结果。它是一种非常常见的调光模型,从游戏到电影都有诸多应用。虽然在镜面反射的精确建模上它并不是最接近现实的,但在大多数情况下它都显得极为逼真。另外,如果你的观察对象是远离相机的而且不需要对高光进行精确计算的时候,Phong高光模型是表现着色器高光效果最好的方式之一。
Unity已经为我们提供了一系列可以使用的光照函数,但是为了正确地使用它们,你还必须使用相对应的正确参数。参照下面的表格:
| 类型 | 函数参数 |
| 非视点相关型 | half4 Lighting+你选择的函数名(SurfaceOutput s, half3 lightDir, half atten) |
| 视点相关型 | half4 Lighting+你选择的函数名(SurfaceOutput s, half3 lightDir, half3 viewDir, half atten) |
一、创建Shader
Shader "Custom/ShaderPhong" {
Properties {
_MainTint ("Diffuse Tint", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_MainTex ("Base (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}
_SpecularColor ("Specular Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_SpecPower ("Specular Power", Range(0, 30)) = 1
}
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }
LOD 200
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf Phong
float4 _SpecularColor;
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTint;
float _SpecPower;
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
//自定义光照模型(Phong高光)
inline fixed4 LightingPhong (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, half3 viewDir, fixed atten)
{
//漫反射组件(diff) = 顶点法线与光的入射方向的点积
//diff=1 : 表明物体是正对着光源方向的
//diff=-1 : 表明物体是背对着光源方向的
float diff = dot(s.Normal, lightDir);
//反射向量(reflectionVector)
//先对顶点法线向量值进行缩放,将该值乘以2.0后再乘以diff值,得到的值减去光照的方向向量值。
//这样做的原因是为了实现法线朝向光源弯曲的效果,所以作为一个远离光源的法线向量,它将被强制朝向光源方向。
float3 reflectionVector = normalize(2.0 * s.Normal * diff - lightDir);
float spec = pow(max(0, dot(reflectionVector, viewDir)), _SpecPower);
float3 finalSpec = _SpecularColor.rgb * spec;
fixed4 c;
c.rgb = (s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * diff) + (_LightColor0.rgb * finalSpec);
c.a = 1.0;
return c;
}
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {
half4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex);
o.Albedo = c.rgb;
o.Alpha = c.a;
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Diffuse"
}
二、创建Plane、Material
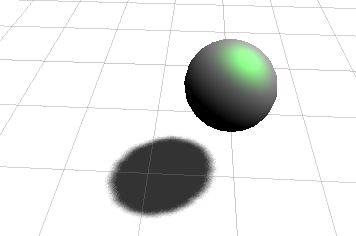
运行效果
评论:
发表评论: