示例:结构数组
post by:追风剑情 2020-4-17 9:46
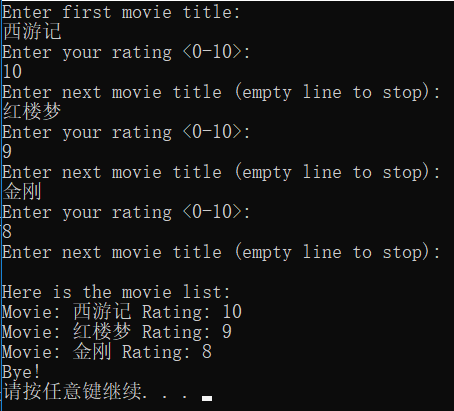
示例:让用户输入看过的电影
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//提供CHAR_BIT的定义,CHAR_BIT表示每字节的位数
#include <limits.h>
//C99定义了bool、true、false
#include <stdbool.h>
#define TSIZE 45 //储存片名的数组大小
#define FMAX 5 //影片的最大数量
struct film {
char title[TSIZE]; //影片名称
int rating; //评级(0~10)
};
char* s_gets(char* st, int n);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct film movies[FMAX];
int i = 0;
int j;
puts("Enter first movie title:");
while (i < FMAX && s_gets(movies[i].title, TSIZE) != NULL &&
movies[i].title[0] != '\0')
{
puts("Enter your rating <0-10>:");
scanf("%d", &movies[i++].rating);
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
puts("Enter next movie title (empty line to stop):");
}
if (i == 0)
printf("No data entered.");
else
printf("Here is the movie list:\n");
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
printf("Movie: %s Rating: %d\n", movies[j].title, movies[j].rating);
printf("Bye!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// 自己实现读取函数
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* ret_val;
int i = 0;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val) //即,ret_val != NULL
{
while (st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0')
i++;
if (st[i] == '\n')
st[i] = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
}
运行测试
评论:
发表评论: