C语言—strcmp()
post by:追风剑情 2019-10-29 19:40
strcmp()函数用来比较两个字符串内容是否相等。
示例: 比较字符串
//Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
//否则只能使用scanf_s()
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
//引入字符串函数string.h
//一些ANSI之前的系统使用strings.h头文件,而
//有些系统可能根本没有字符串头文件。
#include <string.h>
#define ANSWER "Grant"
#define SIZE 40
char * s_gets(char * st, int n);
//argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char try[SIZE];
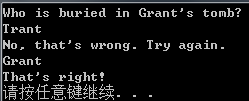
puts("Who is buried in Grant's tomb?");
s_gets(try, SIZE);
//try != ANSWER 比较的是字符串地址
//strcmp() 比较的是字符串内容
//while (strcmp(try, ANSWER)) 也可以这样写
while (strcmp(try, ANSWER) != 0)
{
puts("No, that's wrong. Try again.");
s_gets(try, SIZE);
}
puts("That's right!");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
char * s_gets(char * st, int n)
{
char * ret_val;
int i = 0;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val) //即,ret_val != NULL
{
while (st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0')
i++;
if (st[i] == '\n')
st[i] = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
}
示例:strcmp()的返回值
//Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
//否则只能使用scanf_s()
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
//引入字符串函数string.h
//一些ANSI之前的系统使用strings.h头文件,而
//有些系统可能根本没有字符串头文件。
#include <string.h>
//argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/*
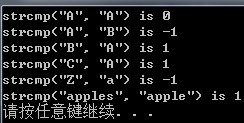
ASCII 标准规定,如果第1个字符串在第2个字符串前面,strcmp()返回一个负数;
如果两个字符串相同,strcmp()返回0;
如果第1个字符串在第2个字符串后面,strcmp()返回正数。
然而,返回的具体值取决于编译器的实现,有的编译器返回ASCII码之差。
*/
printf("strcmp(\"A\", \"A\") is ");
printf("%d\n", strcmp("A", "A"));
printf("strcmp(\"A\", \"B\") is ");
printf("%d\n", strcmp("A", "B"));
printf("strcmp(\"B\", \"A\") is ");
printf("%d\n", strcmp("B", "A"));
printf("strcmp(\"C\", \"A\") is ");
printf("%d\n", strcmp("C", "A"));
printf("strcmp(\"Z\", \"a\") is ");
printf("%d\n", strcmp("Z", "a"));
printf("strcmp(\"apples\", \"apple\") is ");
printf("%d\n", strcmp("apples", "apple"));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
示例:判断用户输入
//Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
//否则只能使用scanf_s()
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
//引入字符串函数string.h
//一些ANSI之前的系统使用strings.h头文件,而
//有些系统可能根本没有字符串头文件。
#include <string.h>
#define SIZE 80
#define LIM 10
#define STOP "quit"
char * s_gets(char * st, int n);
//argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char input[LIM][SIZE];
int ct = 0;
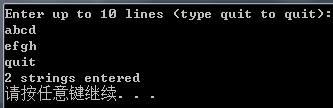
printf("Enter up to %d lines (type quit to quit):\n", LIM);
while (ct < LIM && s_gets(input[ct], SIZE) != NULL &&
strcmp(input[ct], STOP) != 0 &&
input[ct][0] != '\0')
{
ct++;
}
printf("%d strings entered\n", ct);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
char * s_gets(char * st, int n)
{
char * ret_val;
int i = 0;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val) //即,ret_val != NULL
{
while (st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0')
i++;
if (st[i] == '\n')
st[i] = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
}
评论:
发表评论: