委托——Delegate.CreateDelegate()
post by:追风剑情 2019-7-8 16:02
示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Reflection;
namespace ReflectionMethodsCache
{
class Program
{
//将方法缓存为委托,比通过反射调用Invoke()效率高
public delegate void Fun1();
public delegate void Fun2(string arg);
public delegate void Fun3();
public delegate void Fun4();
public static Fun1 f1;
public static Fun2 f2;
public static Fun3 f3;
public static Fun4 f4;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type type = typeof(ClassA);
//firstArgument=null,则把委托作为static方法
MethodInfo methodInfo = type.GetMethod("Fun1");
if (methodInfo != null)
{
f1 = (Fun1)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeof(Fun1), null, methodInfo);
f1();
}
methodInfo = type.GetMethod("Fun2");
if (methodInfo != null)
{
f2 = (Fun2)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeof(Fun2), null, methodInfo);
f2("xxx");
}
methodInfo = type.GetMethod("Fun3");
if (methodInfo != null)
{
f3 = (Fun3)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeof(Fun3), null, methodInfo);
f3();
}
//用指定的实例方法创建委托,这样创建出来的委托可访问实例变量
ClassA classA = new ClassA();
classA.i = 50;
type = classA.GetType();
methodInfo = type.GetMethod("Fun1");
if (methodInfo != null)
{
f1 = (Fun1)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeof(Fun1), classA, methodInfo);
f1();
}
methodInfo = type.GetMethod("Fun4");
if (methodInfo != null)
{
f4 = (Fun4)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeof(Fun4), classA, methodInfo);
f4();//此委托可访问classA中的实例变量
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class ClassA
{
public int i = 0;
public void Fun1()
{
Console.WriteLine("call Fun1");
}
public void Fun2(string arg)
{
Console.WriteLine("call Fun2, arg={0}", arg);
}
public static void Fun3()
{
Console.WriteLine("call static Fun3");
}
public void Fun4()
{
Console.WriteLine("call Fun4, i={0}", i);
}
}
public class ClassB
{
}
}
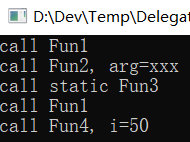
运行测试
评论:
发表评论: