语言集成查询 (LINQ)
post by:追风剑情 2019-6-28 16:18
示例一:从数组中查询数据
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace LINQ
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//数组隐式支持泛型IEnumerable<T>接口
int[] scores = new int[] { 97, 92, 81, 60 };
//这句仅创建查询变量,不会执行查询
//查询变量本身只存储查询命令,实际的查询执行会延迟到调用foreach时发生
//查询语法查询
IEnumerable<int> scoreQuery =
from score in scores
where score > 80
orderby score
select score;
//对数据按奇偶分组 group by into
IEnumerable<IGrouping<int, int>> scoreQuery2 =
from score in scores
where score > 80
let g = score % 2 //通过let标识符存储计算结果
group score by g into scoreGroup
orderby scoreGroup.Key
select scoreGroup;
//调用ToList()或ToArray()会立即执行查询并缓存其结果
int[] scoreQueryCache =
(from score in scores
where score > 80
orderby score
select score).ToArray();
List<int> scoreQueryCache1 =
(from score in scores
where score > 80
orderby score
select score).ToList();
//方法语法查询
//Where()等其他查询方法都是扩展方法
//Lambda表达式 score => score > 80
IEnumerable<int> scoreQuery1 = scores.Where(score => score > 80).OrderBy(n => n);
//IEnumerable<T>查询编译为委托
//IQueryable和IQueryable<T>查询编译为表达式树
//IQueryable<T>派生自IEnumerable<T>
//在调用foreach之前不会执行查询
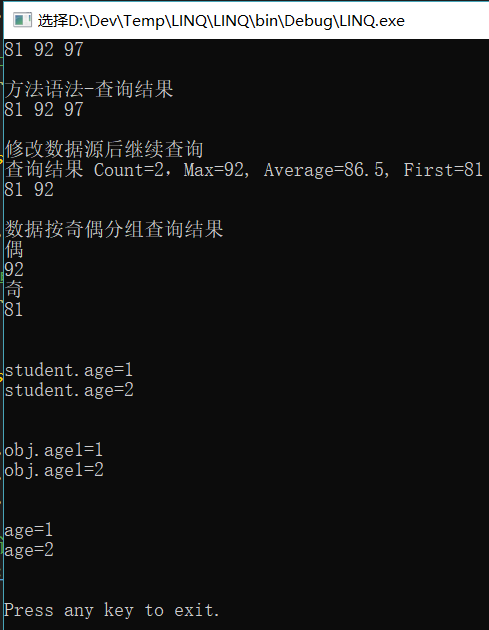
Console.WriteLine("查询语法-查询结果");
foreach (int i in scoreQuery)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine(System.Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine("方法语法-查询结果");
foreach (int i in scoreQuery1)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine(System.Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine("修改数据源后继续查询");
scores[0] = 59;
//这些查询方法会导致执行查询
int count = scoreQuery.Count(); //个数
int max = scoreQuery.Max(); //最大值
double average = scoreQuery.Average();//平均值
int first = scoreQuery.First();//第1个元素
Console.WriteLine("查询结果 Count={0},Max={1}, Average={2}, First={3}",
count, max, average, first);
foreach (int i in scoreQuery)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine(System.Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine("数据按奇偶分组查询结果");
foreach (var groupOfScores in scoreQuery2)
{
Console.WriteLine(groupOfScores.Key == 1 ? "奇" : "偶");
foreach (int i in groupOfScores)
{
Console.WriteLine(i + " ");
}
}
//建议尽量使用查询语法,只在必需的情况下才使用方法语法,
//两者在性能上没有区别,只是查询语法更易读。
Console.WriteLine(System.Environment.NewLine);
/* 使用LINQ查询非泛型IEnumerable集合(如ArrayList) */
ArrayList arrList = new ArrayList();
arrList.Add(new Student() { age = 1 });
arrList.Add(new Student() { age = 2 });
//非泛型数据源必需指定类型 Student s
var query = from Student s in arrList select s;
foreach (Student s in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("student.age={0}", s.age);
}
Console.WriteLine(System.Environment.NewLine);
//select可以返回新对象,这样可以重新定义字段
var query1 = from Student s in arrList select new { age1 = s.age};
foreach (var s in query1)
{
Console.WriteLine("obj.age1={0}", s.age1);
}
Console.WriteLine(System.Environment.NewLine);
//只返回单个字段
var query2 = from Student s in arrList select s.age ;
foreach (var age in query2)
{
Console.WriteLine("age={0}", age);
}
Console.WriteLine(System.Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
//更多查询关键字
//https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/previous-versions/bb310804%28v%3dvs.110%29
}
}
public class Student
{
public int age;
}
}
运行测试
评论:
发表评论: